[leetcode] Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II
Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II
Algorithm: 트리 level: 2 link: https://leetcode.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node-ii/
Given a binary tree
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
Follow up:
- You may only use constant extra space.
- Recursive approach is fine, you may assume implicit stack space does not count as extra space for this problem.
Example 1:
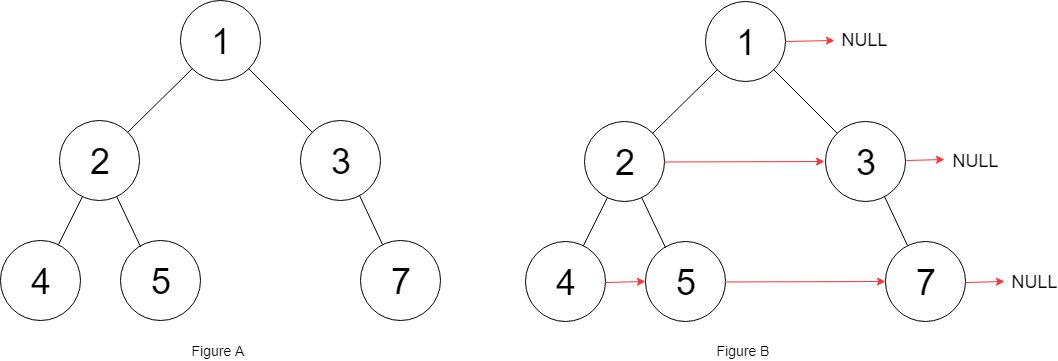
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,7]
Output: [1,#,2,3,#,4,5,7,#]
Explanation: Given the above binary tree (Figure A),
your function should populate each next pointer to point to its next right node,
just like in Figure B.
The serialized output is in level order as connected by the next pointers,
with '#' signifying the end of each level.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the given tree is less than
6000. -100 <= node.val <= 100
---
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node* next;
Node() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {}
Node(int _val) : val(_val), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {}
Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right, Node* _next)
: val(_val), left(_left), right(_right), next(_next) {}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
Node * prev = NULL;
if(root == NULL) return root;
queue <Node *> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
int n = q.size();
Node * top;
//자식의 갯수 만큼
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
top = q.front();
q.pop();
if(prev != NULL){
prev->next = top;
}
prev = top;
if(top->left) q.push(top->left);
if(top->right) q.push(top->right);
}
top->next = NULL;
prev = NULL;
}
return root;
}
};
-
문제 풀이
BFS로 접근했다
레벨마다 NULL값을 넣어줘야 하기 때문에 자식 PUSH를 모두 한 후에 자식의 갯수만큼 연산을 진행 해 주었다.
-
후기
오늘 일찍 일어난거 칭찬해 :good: